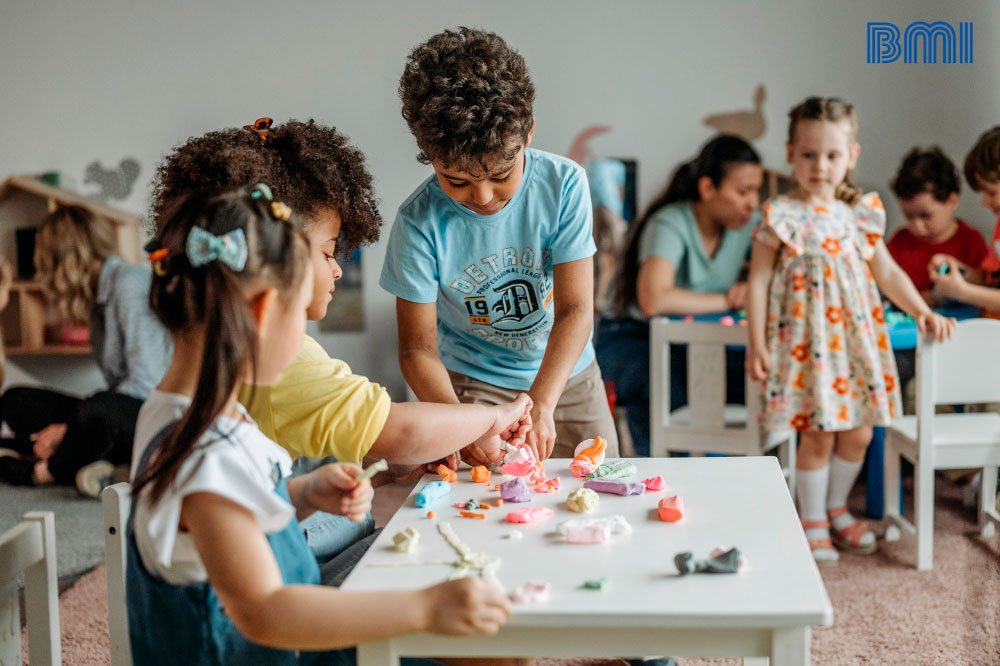
The entrance to classes of children exposes them to a series of viruses and bacteria typical of the relationship between them and of new environments. The most common are diseases transmitted by viruses such as influenza, diarrhea and more complex diseases such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
These types of diseases affect the minor's immune system in the short term, however, they also allow him to create defenses and develop antibodies for the next contacts with these entities.

The main causes of colds are usually viruses that are transmitted by physical contact, as well as by a child who is sick with the virus sneezing or coughing, even if they are not showing symptoms at the time, which is the incubation phase. of it, known as the most contagious.
Stomach diseases are usually caused mainly by children's lack of hygiene when eating, who are usually playing and put food in their mouths without first washing their hands. They also occur because they are found in slightly dirtier areas such as playgrounds or in contact with shared toys.
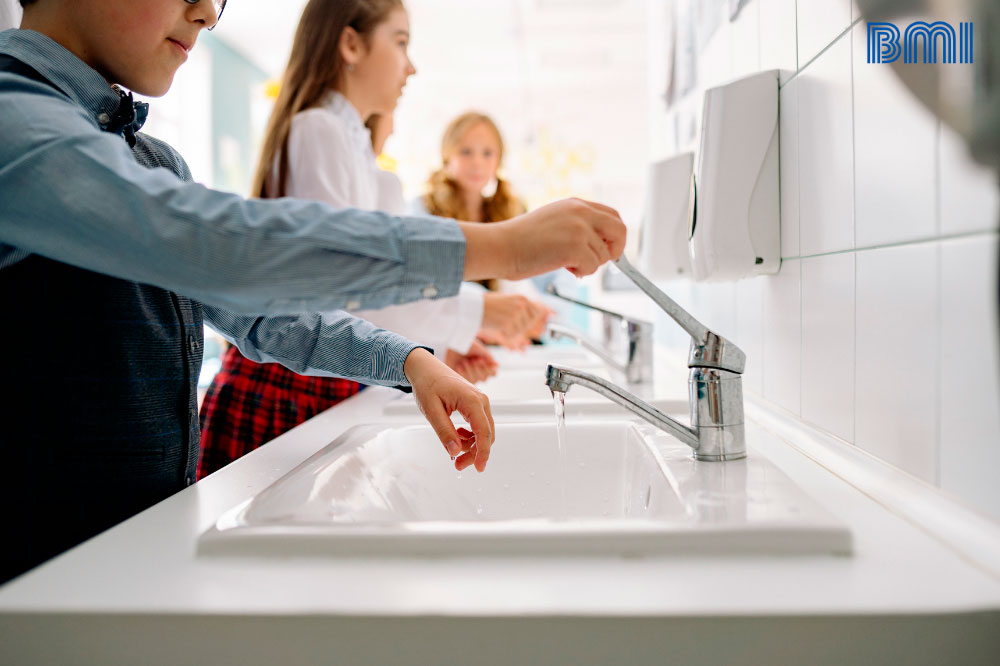

Prevention of the transmission of viruses and bacteria in children can be achieved with simple hygiene habits for them and with the help of supplements that strengthen the immune system.
Some practices to prevent these infections are:
• Do not send sick children to school.
• Teach children to wash their hands correctly and make it fun so that they incorporate it into their daily routines even outside the home.
• Check the children's vaccination schedule so that it is complete according to age.
• Provide them with a balanced diet and adequate rest.
These small actions prevent diseases at this time of year in children and also prevent contagion to the adults who live with them.